Types of Data Backup: Full, Differential, Incremental
Visits: 1134
In today's digital age, backing up data is crucial to ensure you don't lose important information. There are different ways to back up your data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. This article will explain the three main types of data backup: full, differential, and incremental. We'll keep it simple so that anyone, even those who are not tech-savvy, can understand.
1. Full Backup
A full backup is exactly what it sounds like: a complete copy of all your data. This is the most straightforward type of backup.
How it works:
- All files and folders are copied.
- It takes the most time and space because everything is backed up.
Pros:
- Easy to restore because all data is in one place.
- Simple to manage.
Cons:
- Requires a lot of storage space.
- Takes longer to complete.
Example: Imagine you have 10 GB of data. A full backup will copy all 10 GB every time you back up your data.
| Feature | Full Backup |
|---|---|
| Backup Time | Long |
| Storage Space | Large |
| Restore Speed | Fast |
| Complexity | Simple |
| Frequency | Can be infrequent |
2. Differential Backup
A differential backup saves all the changes made since the last full backup. It's like taking a snapshot of the differences.
How it works:
- First, a full backup is taken.
- Subsequent backups only include changes made since the last full backup.
Pros:
- Faster than full backups.
- Uses less storage than full backups.
Cons:
- Restoring can take longer because you need the last full backup and the last differential backup.
- Still grows larger over time until the next full backup.
Example: If you start with a 10 GB full backup and add 2 GB of new data, the differential backup will only be 2 GB.
| Feature | Differential Backup |
|---|---|
| Backup Time | Moderate |
| Storage Space | Moderate |
| Restore Speed | Moderate |
| Complexity | Moderate |
| Frequency | Weekly or daily |
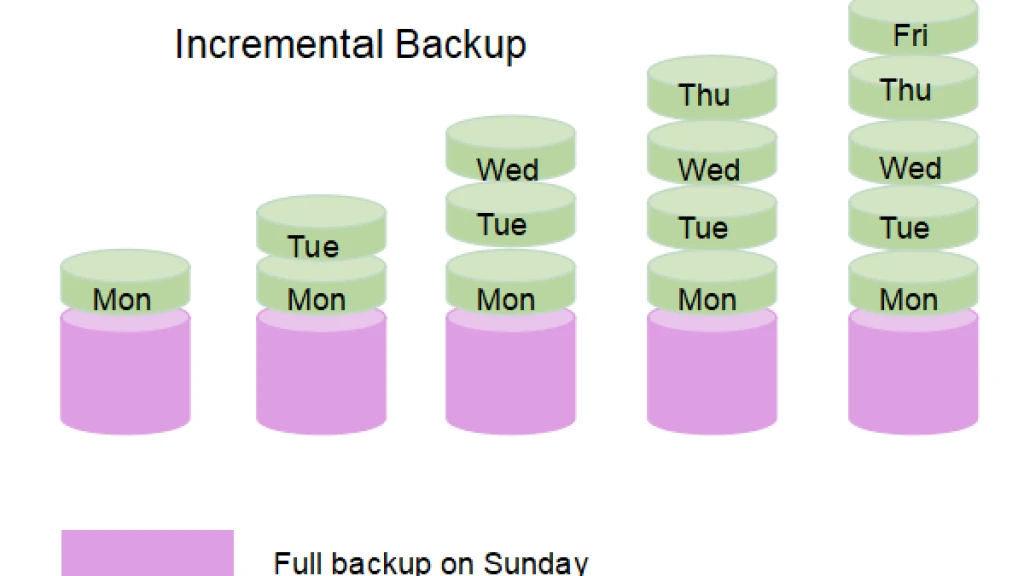
3. Incremental Backup
An incremental backup only saves the data that has changed since the last backup of any type (full, differential, or incremental).
How it works:
- First, a full backup is taken.
- Subsequent backups only include changes since the last incremental backup.
Pros:
- Fastest backup type.
- Uses the least storage space.
Cons:
- Restoring can be slow because you need the last full backup and all incremental backups.
- More complex to manage.
Example: If you start with a 10 GB full backup, add 1 GB of new data, then add another 1 GB the next day, each incremental backup will only be 1 GB.
| Feature | Incremental Backup |
|---|---|
| Backup Time | Short |
| Storage Space | Smallest |
| Restore Speed | Slow |
| Complexity | Complex |
| Frequency | Daily or more often |
Which Backup Should You Use?
Choosing the right type of backup depends on your needs:
- Full Backup: Best for simplicity and easy restores but requires more storage and time.
- Differential Backup: A good balance between speed and storage but requires periodic full backups to stay efficient.
- Incremental Backup: Best for saving time and storage space but can be complex and slow to restore.
Summary Table
Here's a quick comparison of the three types of backups:
| Backup Type | Backup Time | Storage Space | Restore Speed | Complexity | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full | Long | Large | Fast | Simple | Infrequent |
| Differential | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Weekly or daily |
| Incremental | Short | Smallest | Slow | Complex | Daily or more often |
Backing up your data is like insurance for your digital life. By understanding the different types of backups, you can choose the best method to keep your data safe. Remember, it's not a question of if you will need a backup, but when. So, start backing up your data today!
- All Categories
- Basics of the Internet 21
- Internet Security and Privacy 18
- VPN and Protection Tools 23
- Optimizing Internet Performance 15
- Device and Software Management 17
- Wi-Fi and Home Networks 15
- Data backup 16
- Social Media and Security 16
- Cloud Technologies and Storage 18
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices 14
- Linux 16
- Mobile security 15
- Setting up home networks 14
- Digital Legacy 14
- IT Education 15
- Cyber threats 17
- File sharing and security 15
- The future of technology 14
